二叉树最大宽度
662. 二叉树最大宽度
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。
树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。
每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,这些 null 节点也计入长度。
题目数据保证答案将会在 32 位 带符号整数范围内。
示例 1:
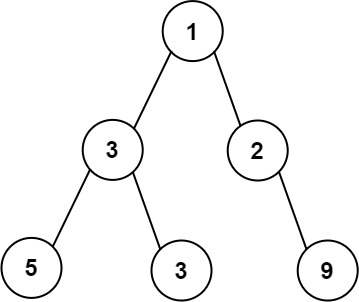
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
输出:4
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 3 层,宽度为 4 (5,3,null,9) 。示例 2:
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7]
输出:7
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 4 层,宽度为 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7) 。示例 3:
输入:root = [1,3,2,5]
输出:2
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 2 层,宽度为 2 (3,2) 。提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[1, 3000] -100 <= Node.val <= 100
层序遍历
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int res = 1; // 初始化最大宽度为1
Queue<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 用于存储当前层的节点及其索引。注意Pair类。
queue.offer(new Pair<>(root, 1)); // 根节点的索引为1。注意初始化Pair实例的方法。
// 使用广度优先搜索(BFS)遍历二叉树
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
int start = queue.peek().getValue(); // 当前层的起始索引
int end = queue.peek().getValue(); // 当前层的结束索引,初始化为起始索引
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> pair = queue.poll();
TreeNode node = pair.getKey();
int index = pair.getValue();
// 更新当前层的结束索引
end = index;
// 将子节点及其索引加入队列
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(new Pair<>(node.left, index * 2));
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(new Pair<>(node.right, index * 2 + 1));
}
}
// 计算当前层的宽度,并更新最大宽度
res = Math.max(res, end - start + 1);
}
return res; // 返回最大宽度
}
}- 时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。需要遍历所有节点。
- 空间复杂度: O(n)。广度优先搜索的空间复杂度最多为 O(n) 。
有返回值有信息参数的DFS
使用哈希表记录每一层最左边节点的索引,计算本层、左右子树的最远距离,返回最大值。
class Solution {
// 使用哈希表记录每一层最左边节点的索引
Map<Integer, Integer> levelMin = new HashMap<>();
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
// 调用深度优先搜索方法。注意index是1,这样左子节点的索引才是index*2。深度无所谓。
return dfs(root, 1, 1);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode node, int depth, int index) {
// 如果节点为空,返回0
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
// 将当前层的最左节点索引记录下来(如果未记录),注意putIfAbsent
levelMin.putIfAbsent(depth, index);
// 计算当前层的最远距离:当前节点索引 - 当前层最左节点的索引 + 1
int currentWidth = index - levelMin.get(depth) + 1;
// 递归计算左右子树的最远距离。索引是无条件增加的,即空节点也有索引。
int leftWidth = dfs(node.left, depth + 1, index * 2);
int rightWidth = dfs(node.right, depth + 1, index * 2 + 1);
// 返回最远距离。左右子树的深度可能不一样,进而右子树的最远距离也未必大于左子树的最远距离,
// 所以需要取左右子树的最远距离的最大值。当前节点也可能没有左右子树,所以最大值有可能是当前节点的最远距离。
return Math.max(currentWidth, Math.max(leftWidth, rightWidth));
}
}- 时间复杂度: O(n) ,其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。需要遍历所有节点。
- 空间复杂度: O(n) 。递归的深度最多为 O(n) 。